What is OGSIVEO?
OGSIVEO is the first and only FDA-approved treatment for adults with progressing desmoid tumors who require a medicine by mouth or injection (systemic therapy). It is not known if OGSIVEO is safe and effective in children.1
Medical experts recommend nirogacestat (OGSIVEO) as a treatment option for desmoid tumors.2
Actor portrayal. Individual results may vary.
OGSIVEO: Studied in a broad range of patients with desmoid tumors in the largest completed clinical trial of its kind
The goals of the trial were to assess the benefits, safety, and tolerability of OGSIVEO in the treatment of adult patients with growing desmoid tumors.1
- The trial compared OGSIVEO to placebo (a pill with no active medicine) in 142 adults
- 70 people were randomly assigned to receive OGSIVEO, and the remaining 72 people were randomly assigned to receive placebo
- Neither the people in the trial nor their doctors knew whether they were getting OGSIVEO or placebo
- People didn’t find out whether they were taking OGSIVEO or placebo until they left the trial (due to either their desmoid tumor progressing, side effects, or other reasons)1
More information about the patients in the OGSIVEO trial
All of the people who participated in the clinical trial:1,3
- Were 18 years of age or older
- Had desmoid tumors that grew larger (20% or more) over the past 12 months
- Fell into one of these categories:
- Had not received any treatment and were not candidates for surgery
- Had their tumors come back after treatment
- Had tumors that were not responsive to treatment
Of the people in the clinical trial:1
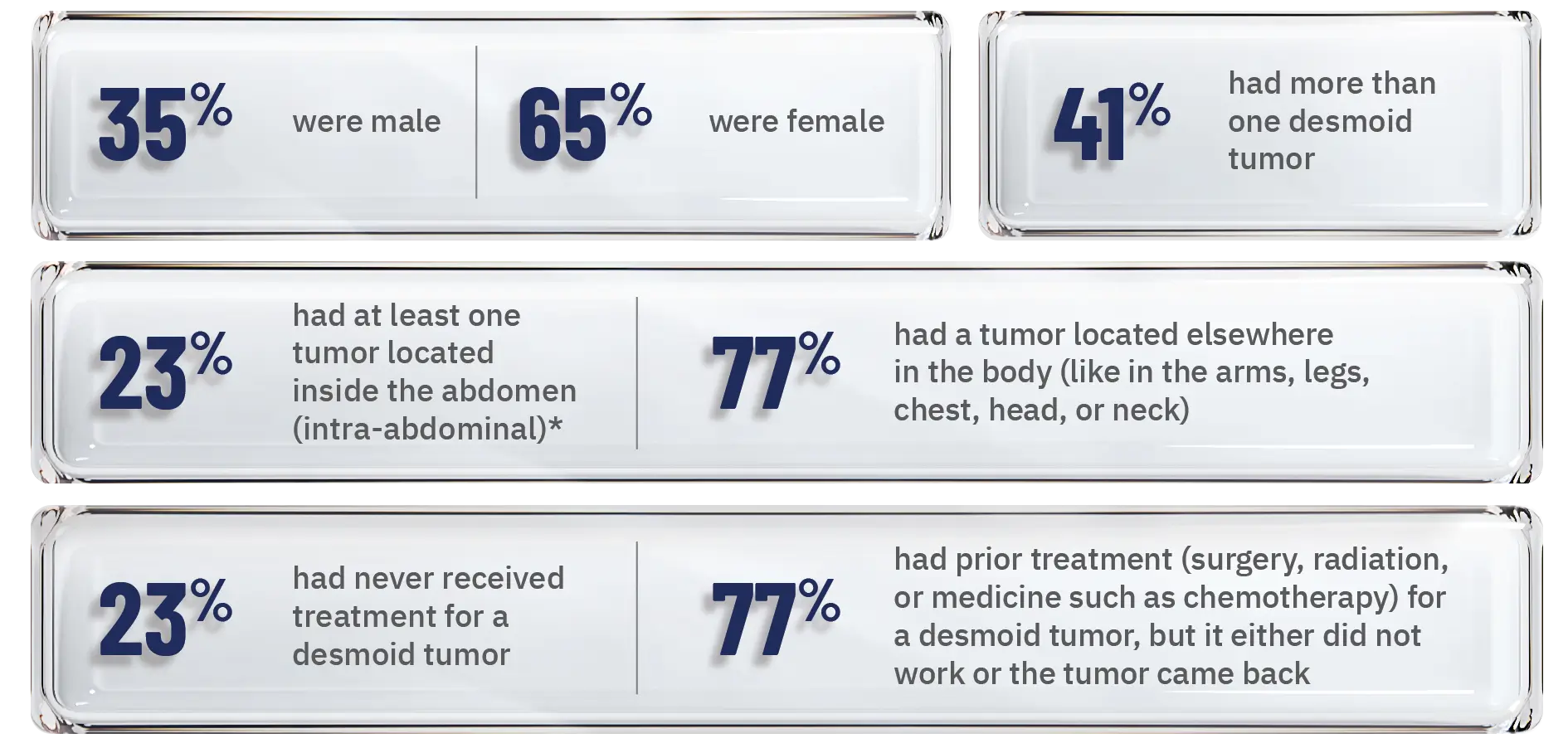
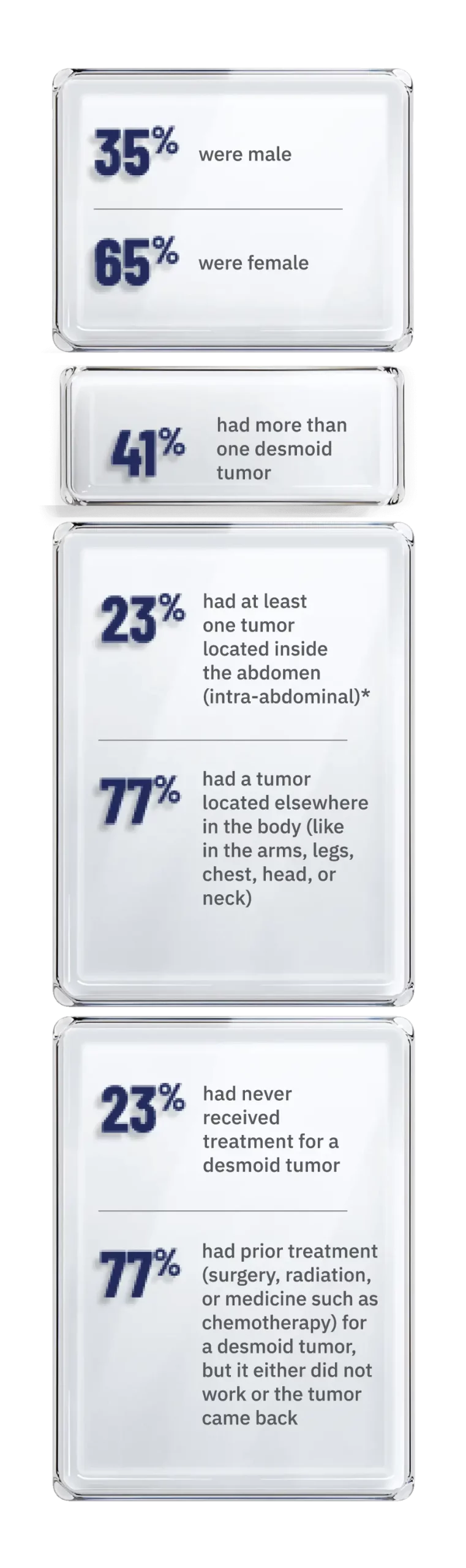
Patients who had multiple desmoid tumors inside the abdomen and elsewhere in the body were classified as having intra-abdominal tumors.
OGSIVEO can help control desmoid tumor progression

In the clinical trial, OGSIVEO reduced the chance of a participant’s disease getting worse during the study by 71% compared with a placebo.
This is known as progression-free survival.1,3
Results with OGSIVEO were generally consistent across different participant characteristics:3
- Gender
- Whether a person had prior treatment for desmoid tumors or not
- Type of prior treatment
- Changes in tumor DNA
- Number and location of tumors
- Family history of familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP)
Limitations: The study was not designed to specifically compare these characteristics and detect differences.
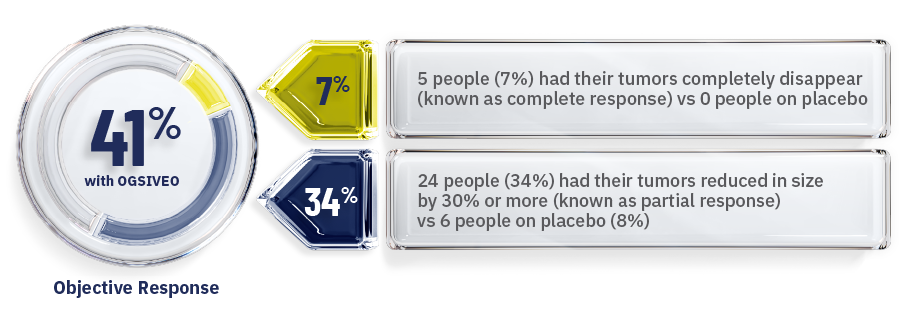
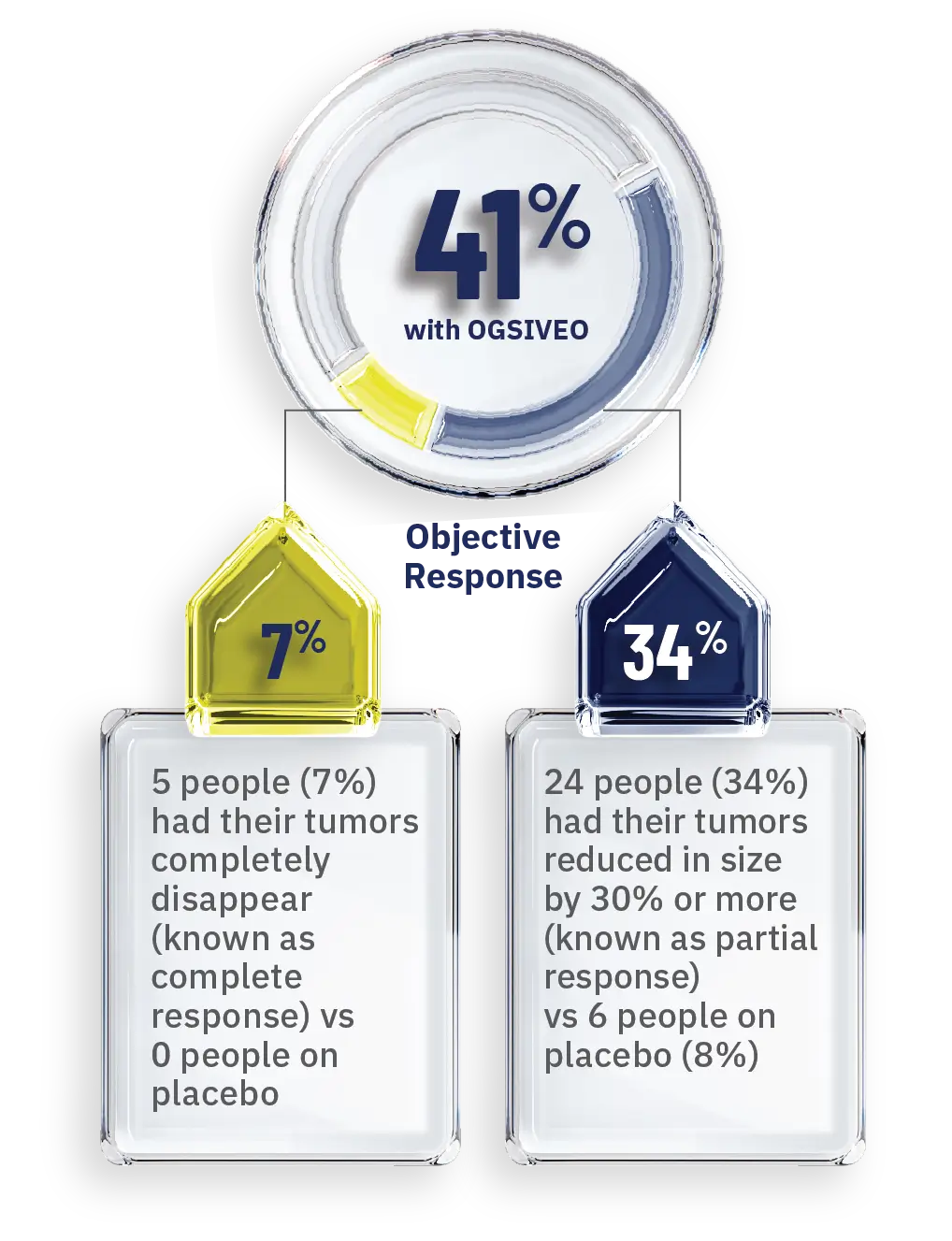
OGSIVEO also helped shrink desmoid tumors or caused them to completely disappear in some people1
Percentage of people whose tumors responded—as confirmed by MRI or CT scans
- When a tumor shrinks by 30% or more or disappears completely, this is known as an objective response.1,3
In patients who responded to OGSIVEO, tumors began to shrink between 2.6 and 19.4 months after starting therapy. The median (middle) amount of time it took for tumors to begin shrinking was 5.6 months, compared to 11.1 months (2.8 to 16.4 months) for patients taking placebo.3
Limitations: This was an exploratory analysis, meaning it was not specifically designed to find differences between OGSIVEO and placebo. Therefore, these results may be due to chance and should be interpreted carefully. Individual results may vary from the clinical trial experience.

People filled out questionnaires at different points during the trial
Patients reported that OGSIVEO reduced pain—one of the most common symptoms of desmoid tumors1
- More than 50% of patients entering the clinical trial had pain. Over the course of the trial, people continued to report their pain
- People taking OGSIVEO reported reductions in worst pain compared with those taking placebo
Limitations: Meaningful changes in pain levels were difficult to estimate in the clinical trial because not all patients completed the pain questionnaires at each timepoint, and because the number of patients completing questionnaires differed between OGSIVEO and placebo treatment groups. Definitive conclusions cannot be made about the impact of OGSIVEO on pain.
OGSIVEO can cause serious side effects, including:1
- Diarrhea
- Ovarian problems
- Liver problems
- New non-melanoma skin cancers
- Electrolyte (salt) problems
OGSIVEO can affect fertility in females and males, which may affect your ability to have a child. Talk to your healthcare provider if this is a concern for you.1
These are not all of the possible side effects of OGSIVEO. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to the FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.1
Learn more possible about side effects at What You May Expect from OGSIVEO >
Need Support?
Our virtual guide is here to help you find the information on this site.
General questions about OGSIVEO
What is OGSIVEO?
OGSIVEO is a prescription medication used to treat adults with progressing desmoid tumors who require a medicine by mouth or injection (systemic therapy). It is not known if OGSIVEO is safe and effective in children.1
OGSIVEO is a systemic therapy, meaning it works throughout the entire body1,8—unlike surgery and radiation which are local therapies, meaning they are typically focused on a single place in the body.9
Is OGSIVEO chemotherapy?
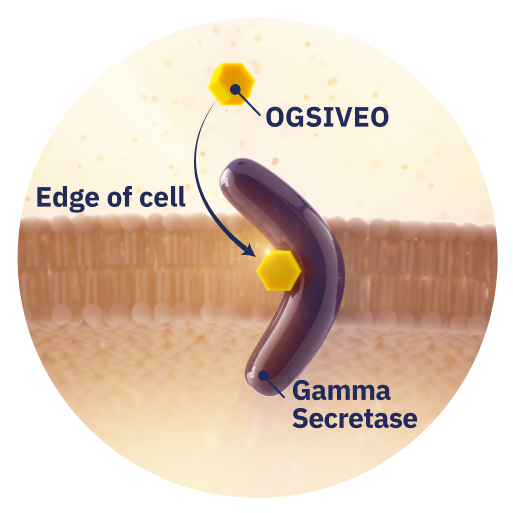
OGSIVEO is not a chemotherapy. It’s a targeted therapy that is thought to work by interfering with gamma secretase—an enzyme that may affect how certain types of cells grow, including desmoid tumor cells.1,9
Is OGSIVEO injected?
No. OGSIVEO is an oral medicine. The tablets are taken by mouth twice a day, with or without food.1
What should I tell my doctor before taking OGSIVEO?
Tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you have liver problems, are pregnant or plan to become pregnant, and if you are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. You should avoid taking proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and H2 blockers during treatment with OGSIVEO. Ask your healthcare provider if you are not sure if you take one of these medicines.1
Is OGSIVEO for anyone with a desmoid tumor?
No. OGSIVEO is for adults with progressing desmoid tumors who require systemic therapy. It is not known if OGSIVEO is safe and effective in children.1 Talk to your doctor to find out if OGSIVEO might be an option for you.
OGSIVEO Stories
Hear from Christina, a real patient treated with OGSIVEO
Learn about the role of OGSIVEO in Christina’s desmoid tumor journey.
This video represents Christina’s personal experience only. Individual results may vary.
Ready to Talk to Your Doctor?
Create a Customized Doctor Discussion Guide
Below are 3 brief questions that you can answer to create a customized Doctor Discussion Guide that can help you prepare for your next appointment.
Here are some tips that may also help you prepare for your conversation:
- Write down your personal experience
- Be specific about your symptoms
- Bring these items to your appointment:
- This guide, either printed or digital form
- A notepad to take notes
- A list of all the medicines you are currently taking, including vitamins and supplements
If you have consented to cookies through our Cookie Settings, we will process your city and state location through cookies and related technologies. This is to allow SpringWorks to understand geographic interests in its products and services. This information will not be used to identify you. The city and state will be shared with service providers who may help SpringWorks to review and aggregate information. If you do not wish to allow tracking of the city and state, you will need to turn off your consent to cookies and refresh your web browser before you begin the Doctor Discussion Guide questions.
References
- OGSIVEO. Prescribing information. SpringWorks Therapeutics, Inc.
- Referenced with permission from the NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) for Soft Tissue Sarcoma V.1.2024. © National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Inc. 2024. All rights reserved. Accessed April 30, 2024. To view the most recent and complete version of the guideline, go online to NCCN.org. NCCN makes no warranties of any kind whatsoever regarding their content, use or application and disclaims any responsibility for their application or use in any way.
- Gounder M, Ratan R, Alcindor T, et al. Nirogacestat, a gamma-secretase inhibitor for desmoid tumors. N Engl J Med. 2023;388(10):898-912.
- Penel N, Chibon F, Salas S. Adult desmoid tumors: biology, management and ongoing trials. Curr Opin Oncol. 2017;29(4):268-274.
- Carothers AM, Rizvi H, Hasson RM, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cell mutations and wound healing contribute to the etiology of desmoid tumors. Cancer Res. 2012;72(1):346-355.
- Villalobos VM, Hall F, Jimeno A, et al. Long-term follow-up of desmoid fibromatosis treated with PF-03084014, an oral gamma secretase inhibitor. Ann Surg Oncol. 2018;25(3):768-775
- Shang H, Braggio D, Lee YJ, et al. Targeting the Notch pathway: a potential therapeutic approach for desmoid tumors. Cancer. 2015;121(22):4088-4096
- NIH. National Cancer Institute. NCI dictionary of cancer terms: systemic therapy. Accessed April 12, 2024. https://www.cancer. gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-terms/def/systemic-therapy
- NIH. National Cancer Institute. Targeted Therapy to Treat Cancer. Accessed April 15, 2024. https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/types/targeted-therapies